Technology has allowed more and more premature infants to not only survive but thrive, growing up to live healthy, normal adult lives.
As medicine continues to advance, smaller and less developed premature infants are being cared for in the NICU. Very low birth weight (VLBW) patients are born weighing less than 1,500 grams (3lb 4oz). These tiny babies cannot be exclusively breastfed as their bodies need higher protein in lower milk volumes compared to full-term infants. This need is typically addressed with fortifiers.
Fortifiers can be derived from bovine (cow) milk or human breast milk; The fortifier is added to mom’s pumped breast milk or processed donor milk and then fed to the VLBW infant.
The idea of using heat treatment to process donor milk was first started in the 1980s and has since expanded to various technologies.
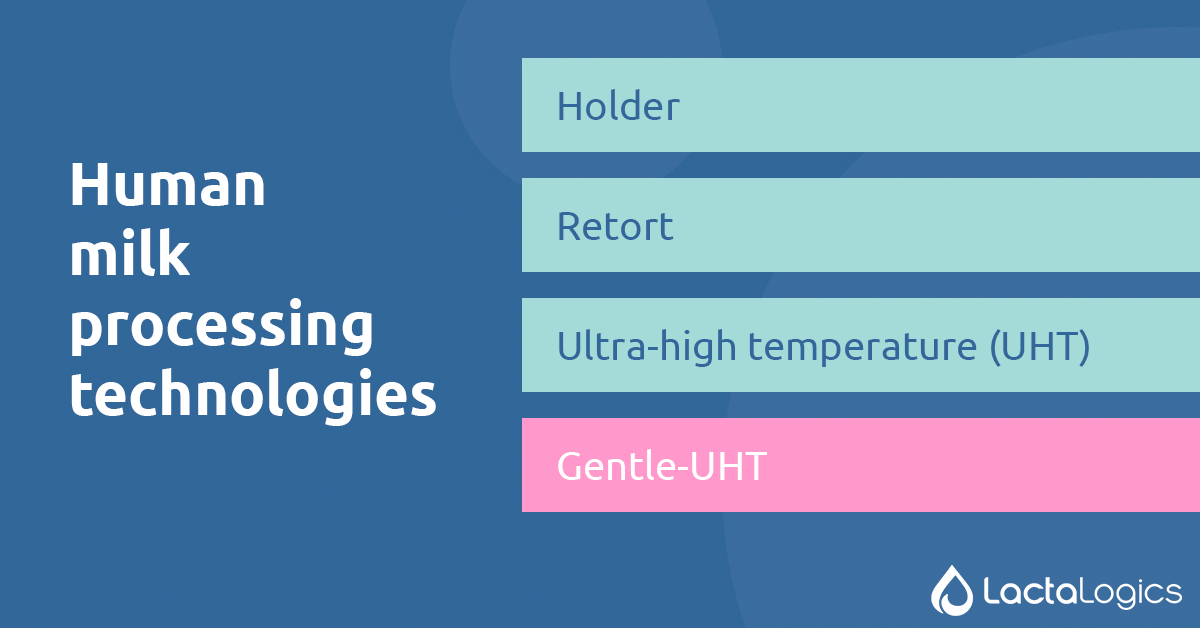
Let’s give an overview of each type of pasteurization
Holder
- Can be called Holder pasteurization or Batch pasteurization
- Human milk is warmed, rapidly cooled, and then frozen until use
- Milk is processed at 145 degrees F for 30 minutes, reducing bacteria but also resulting in a denaturing of proteins (approximately 20-30% of key glycoproteins and immune factors)
- Acts as a shelf extension technology, so cold storage is required
Retort
- Was developed after Holder as a way to address inactivating Bc (Bacillus cereus)
- Human milk is pressure cooked at least over 5 minutes at 250 degrees F, typically for 7-8 minutes
- The vessel that is used to process the milk takes a longer time to heat up and cool down, resulting in a 30% denaturing of key proteins and immune factors
- Produces a commercially sterile, shelf-stable product that inactivates Bc
UHT (Ultra-high temperature)
- Ultra-high temperature processing directly heats the milk for 1–8 seconds at 290+ degrees F, killing bacterial endospores
- Direct heat is accomplished by injecting steam into the milk, then requires the use of a vacuum chamber to remove this steam, denaturing sensitive proteins and immune factors
- Commonly used in the dairy industry
- Creates a shelf-stable product
Gentle-UHT
- A brand new way of processing human milk with high heat applied indirectly to the milk
- High heat protects against bacteria, viruses, molds, and spores including the inactivation of Bc
- Indirectly applying heat leads to superior retention of proteins, immune factors, and HMOs (>90%)
- Gently homogenized to minimize clogging of feeding tubes
- Easy to store and always ready to use, no freezing or thawing required
Until now, innovation has stalled. New emerging technologies, like Gentle-UHT, will help human milk fortification scale, commercialize, and innovate so more babies can receive the amazing benefits of an exclusive human milk diet.